The Venn diagram for plants and animals is a captivating visual representation that showcases the intriguing similarities and distinctions between these two fundamental kingdoms of life. This diagram invites us on an exploration of the shared characteristics, unique features, and overlapping attributes that define plants and animals, unveiling the intricate connections that shape their survival, adaptation, and ecological roles.
Venturing beyond the confines of this diagram, we discover a world of symbiotic relationships and ecological interdependence, where plants and animals engage in dynamic interactions that shape the fabric of ecosystems. From the pollination of flowers to the grazing of herbivores, these interactions highlight the interconnectedness of life and the delicate balance that sustains our planet.
Common Characteristics: Venn Diagram For Plants And Animals
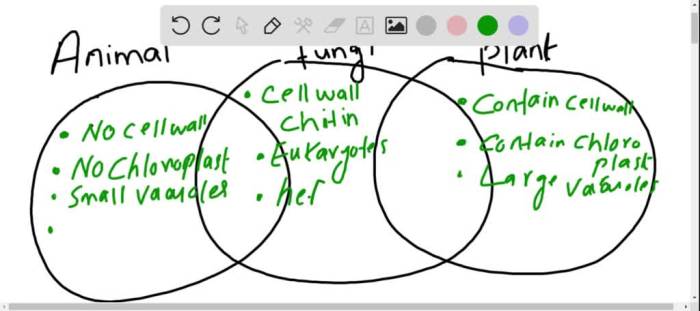
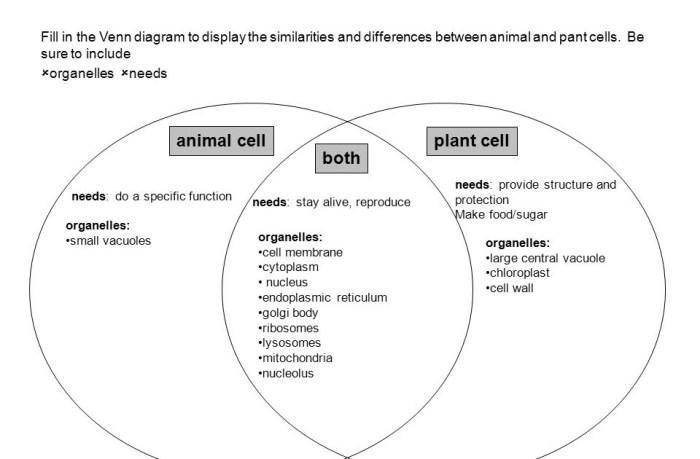
Plants and animals share certain fundamental characteristics that contribute to their survival and adaptation. One of the most significant similarities is the presence of cells. Both plants and animals are composed of cells, which are the basic units of life.
Cells provide the building blocks for tissues, organs, and organ systems, enabling the development and functioning of complex organisms.
Another shared characteristic is the ability to respond to stimuli. Plants and animals can sense and react to changes in their environment. For example, plants exhibit phototropism, the growth towards light, while animals can move in response to touch or danger.
Distinctive Features
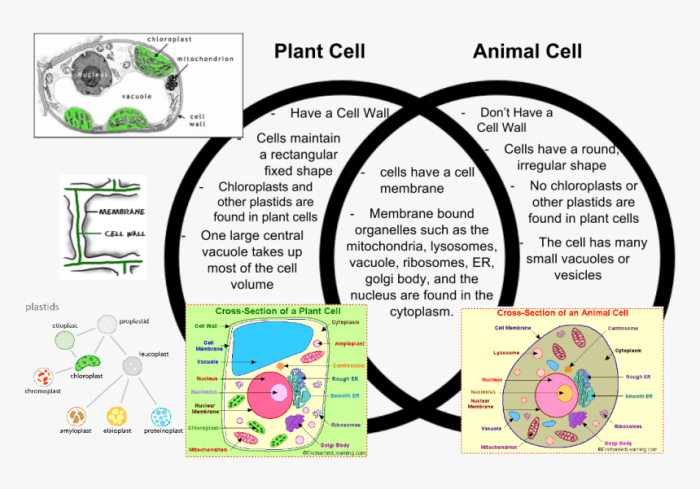
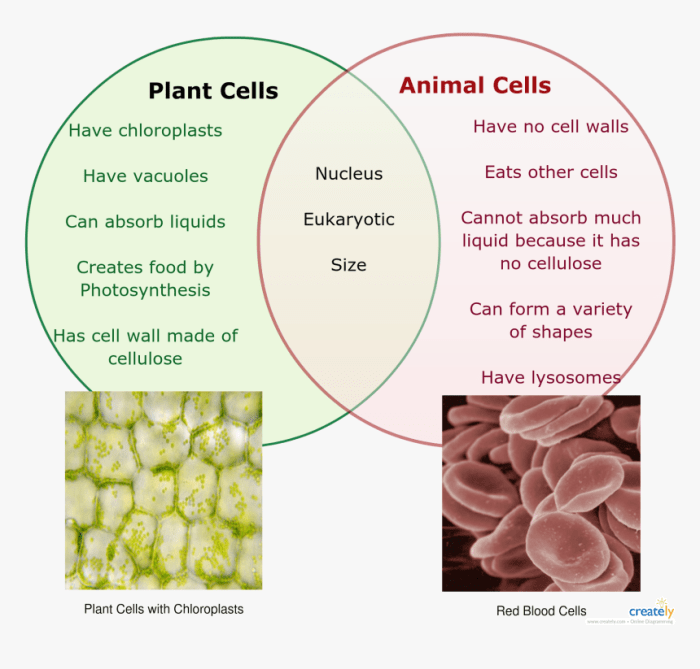
Despite their commonalities, plants and animals also exhibit distinctive features that differentiate them. One of the most notable differences is the presence of a cell wall in plants. The cell wall provides plants with structural support and protection, enabling them to withstand environmental stresses.
Animals, on the other hand, lack cell walls and have more flexible cell membranes.
Another distinguishing characteristic is the mode of nutrition. Plants are autotrophs, meaning they can produce their own food through photosynthesis. Animals, in contrast, are heterotrophs, relying on other organisms for sustenance.
Overlapping Attributes, Venn diagram for plants and animals
In addition to their distinct features, plants and animals also share some overlapping attributes. One such attribute is reproduction. Both plants and animals can reproduce sexually and asexually. Sexual reproduction involves the fusion of gametes, resulting in genetic diversity. Asexual reproduction, on the other hand, involves the production of offspring from a single parent, resulting in genetically identical individuals.
Another overlapping attribute is nutrition. While plants are primarily autotrophic, some plants, such as carnivorous plants, have evolved to supplement their nutrition by trapping and digesting insects. Animals, on the other hand, are heterotrophic but may exhibit variations in their dietary habits, with some animals being herbivores, carnivores, or omnivores.
Symbiotic Relationships
Plants and animals often engage in symbiotic relationships, which can be mutually beneficial or parasitic. One example of a mutually beneficial symbiotic relationship is the relationship between plants and pollinators. Plants provide nectar and pollen to pollinators, such as bees and butterflies, while pollinators assist in the transfer of pollen, facilitating plant reproduction.
A parasitic symbiotic relationship occurs when one organism benefits at the expense of the other. For example, some plants, such as mistletoe, are parasitic and attach themselves to the branches of trees, drawing nutrients from the host plant.
Ecological Interdependence
Plants and animals are ecologically interdependent, playing crucial roles in the functioning of ecosystems. Plants are primary producers, converting sunlight into energy through photosynthesis, which forms the basis of food chains and food webs. Animals, as consumers, rely on plants for food and shelter.
The interactions between plants and animals also contribute to biodiversity. Plants provide habitat and nesting sites for animals, while animals disperse seeds and pollinate plants, facilitating plant reproduction and genetic diversity.
Question Bank
What is the main purpose of a Venn diagram for plants and animals?
A Venn diagram for plants and animals visually represents the shared characteristics and unique features that distinguish these two kingdoms of life.
How do the common characteristics between plants and animals contribute to their survival?
Shared traits such as cellular organization, metabolism, and response to stimuli enhance their ability to adapt and thrive in diverse environments.
What are some examples of symbiotic relationships between plants and animals?
Pollination by insects, seed dispersal by birds, and mutualistic associations between fungi and plants are common examples of symbiotic interactions.