Unit 5: reasoning and organization – reading quiz – Unit 5: Reasoning and Organization in Reading Quiz delves into the intricacies of critical thinking and logical structure, providing a comprehensive understanding of how these elements enhance reading comprehension. By exploring reasoning techniques, text organization, and assessment strategies, this quiz empowers readers to navigate complex texts with confidence and proficiency.
Reasoning and organization are fundamental pillars of effective reading, enabling us to extract meaning, draw inferences, and make informed judgments. This quiz delves into the concepts of inductive and deductive reasoning, the role of analogies, and the significance of text structure in shaping our understanding.
1. Understanding Reasoning and Organization in Reading
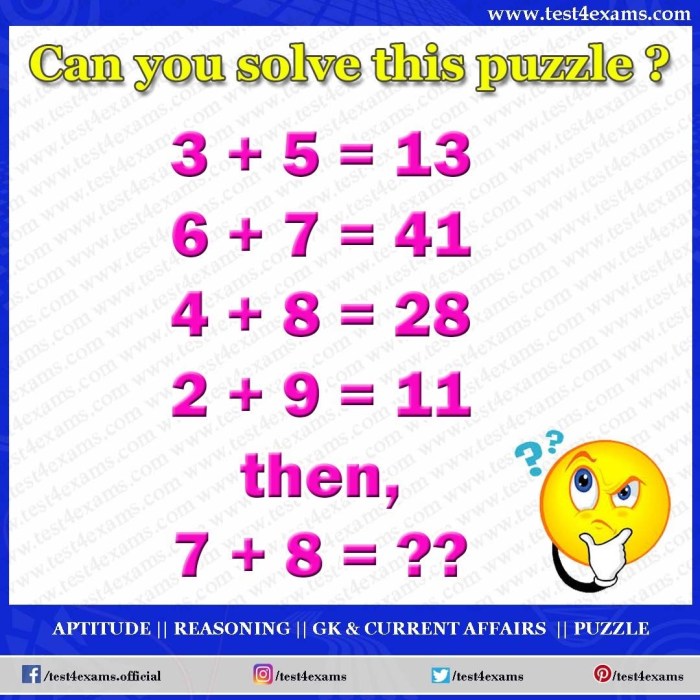
Reasoning and organization are crucial elements in reading comprehension. Reasoning refers to the cognitive process of making inferences, drawing conclusions, and understanding the underlying logic of a text. Organization, on the other hand, involves the logical arrangement of ideas and information within a text, making it easier for readers to follow and comprehend.
2. Identifying Reasoning Techniques in Texts

Inductive Reasoning, Unit 5: reasoning and organization – reading quiz
- Involves drawing general conclusions from specific observations.
- Example: After observing several red cars on the road, you might conclude that most cars are red.
Deductive Reasoning
- Uses general principles or premises to arrive at specific conclusions.
- Example: If all dogs are mammals (premise), and Fido is a dog (premise), then Fido is a mammal (conclusion).
Analogies
- Compare two similar situations or objects to draw inferences.
- Example: The human heart is like a pump that circulates blood.
3. Analyzing Text Structure and Organization
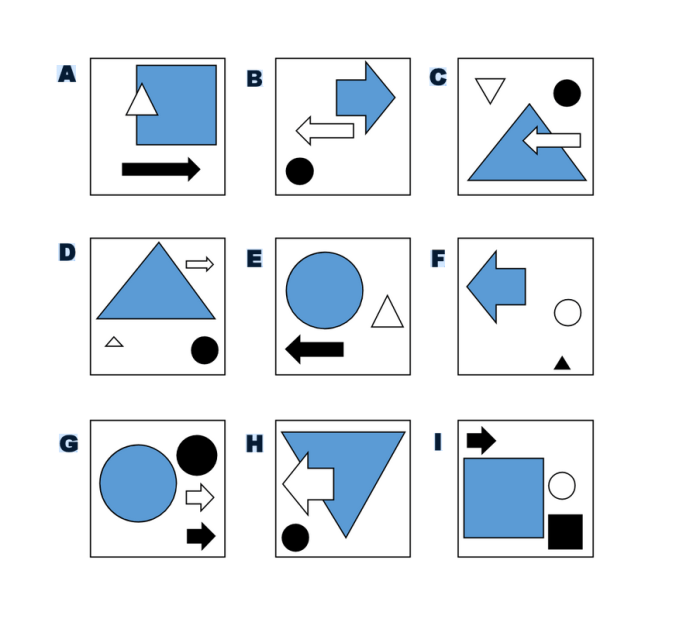
Text structure refers to the way ideas are organized within a text. Common structures include:
- Chronological: Presents events in a sequential order.
- Problem-Solution: Identifies a problem and provides a solution.
Headings, subheadings, and transitions help readers navigate the text and understand its organization.
4. Improving Reasoning and Organization Skills: Unit 5: Reasoning And Organization – Reading Quiz
Inductive Reasoning, Unit 5: reasoning and organization – reading quiz
- Encourage students to make observations and form hypotheses.
- Provide opportunities for them to collect and analyze data.
Deductive Reasoning
- Teach students the principles of logical reasoning.
- Use syllogisms and other deductive exercises to practice.
Organization
- Use HTML table tags to demonstrate logical structure.
- Have students Artikel and summarize texts to improve comprehension.
5. Assessing Reasoning and Organization in Reading
Assessment methods for evaluating reasoning skills include:
- Multiple-choice questions
- Short-answer responses
To evaluate the organization of a text, consider the following:
- Logical flow of ideas
- Clarity and coherence of transitions
A checklist for assessing reasoning and organization in reading can include:
- Identification of reasoning techniques
- Evaluation of text structure
- Assessment of overall organization
FAQ Insights
What is the significance of reasoning in reading?
Reasoning is crucial in reading as it allows readers to make inferences, draw conclusions, and evaluate the validity of arguments presented in the text.
How does text organization impact reading comprehension?
Text organization plays a vital role in comprehension by providing a logical structure that guides readers through the main ideas and supporting details, making it easier to understand and retain information.
What are the different types of reasoning techniques used in reading?
Inductive reasoning involves drawing general conclusions from specific observations, while deductive reasoning applies general principles to specific cases. Analogies are also commonly used to establish relationships and draw comparisons between concepts.