Select all of the correct statements about transcription factors: embark on an enlightening journey into the realm of gene regulation. Transcription factors, the gatekeepers of gene expression, hold the key to understanding cellular processes and unlocking the mysteries of life itself.
Delve into the intricate mechanisms by which transcription factors orchestrate the symphony of gene activity, shaping cellular identity and driving biological processes. From their structural foundations to their dynamic interactions with DNA, cofactors, and chromatin, discover the multifaceted nature of these molecular maestros.
1. Definition and Nature of Transcription Factors
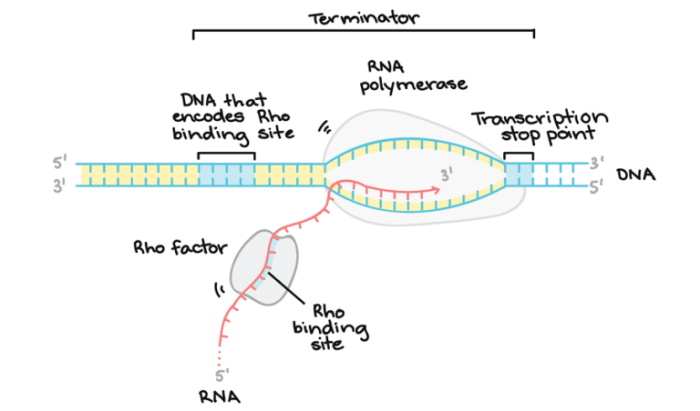
Transcription factors are proteins that regulate gene expression by binding to specific DNA sequences and controlling the transcription of genes. They play a crucial role in cellular processes such as development, differentiation, and homeostasis.
Transcription factors have distinct structural features, including DNA-binding domains, activation domains, and repression domains. These domains enable them to interact with DNA, recruit other proteins, and modulate gene expression.
Examples of different types of transcription factors include:
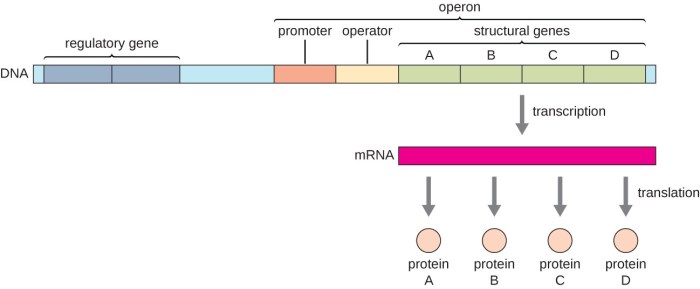
- General transcription factors: Essential for the basal transcription machinery
- Sequence-specific transcription factors: Bind to specific DNA sequences and regulate gene expression
- Ligand-activated transcription factors: Activated by specific ligands, such as hormones or growth factors
2. Mechanisms of Action of Transcription Factors: Select All Of The Correct Statements About Transcription Factors
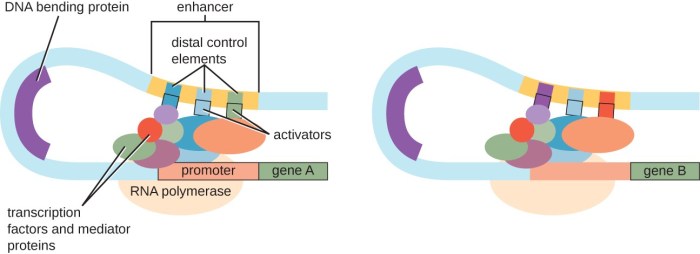
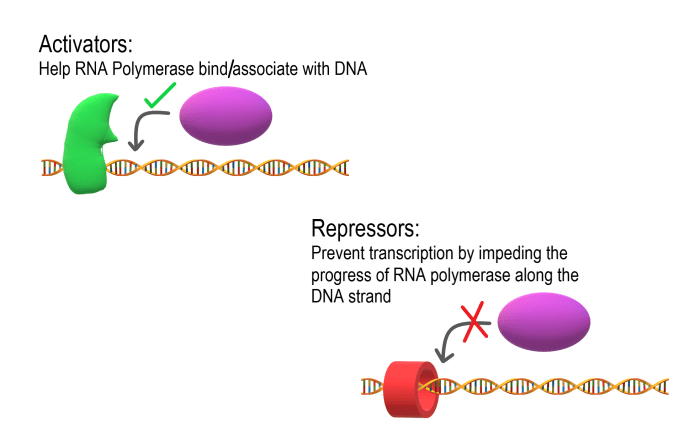
Transcription factors bind to specific DNA sequences known as promoter or enhancer regions. They can activate or repress gene transcription by:
- Recruiting RNA polymerase to the promoter region
- Modifying chromatin structure to make DNA more accessible
- Interfering with the binding of other transcription factors
Cofactors, such as coactivators and corepressors, play a role in regulating transcription factor activity. They can enhance or suppress the ability of transcription factors to bind DNA and modulate gene expression.
3. Regulation of Transcription Factors
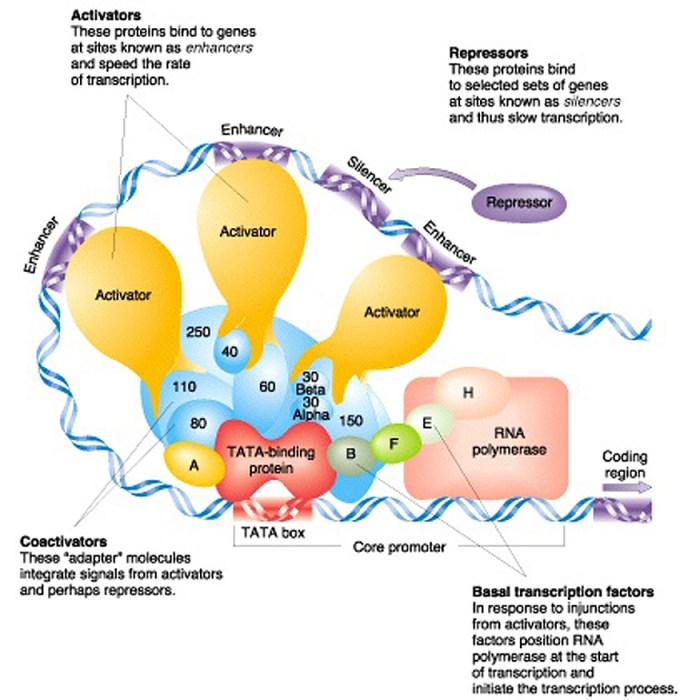
Transcription factor activity is tightly regulated to ensure proper gene expression. Mechanisms of regulation include:
- Post-translational modifications: Phosphorylation, acetylation, and ubiquitination can alter transcription factor activity
- Protein-protein interactions: Interactions with other proteins can modulate transcription factor function
- Cellular signaling pathways: Signaling pathways can activate or inhibit transcription factors
Transcription factors play a crucial role in cellular differentiation and development. They determine which genes are expressed in different cell types, leading to the formation of specialized tissues and organs.
4. Clinical Significance of Transcription Factors
Transcription factors are implicated in various diseases, including:
- Cancer: Mutations in transcription factors can lead to uncontrolled cell growth and proliferation
- Developmental disorders: Defects in transcription factors can cause birth defects and developmental abnormalities
- Neurodegenerative diseases: Dysregulation of transcription factors can contribute to the development of neurodegenerative diseases
Transcription factors are potential targets for therapeutic purposes. Targeting transcription factors can help correct gene expression defects and treat diseases.
Examples of transcription factor-based therapies include:
- Inhibitors of transcription factors involved in cancer
- Gene therapy to introduce functional transcription factors in genetic disorders
Expert Answers
What is the primary function of transcription factors?
Transcription factors regulate gene expression by binding to specific DNA sequences and modulating the activity of RNA polymerase.
How do transcription factors interact with DNA?
Transcription factors possess DNA-binding domains that enable them to recognize and bind to specific nucleotide sequences within the genome.
What are the different types of transcription factors?
There are numerous types of transcription factors, each with unique structural features and target genes, including activators, repressors, and basal factors.
How are transcription factors regulated?
Transcription factors are regulated through various mechanisms, including post-translational modifications, protein-protein interactions, and cellular signaling pathways.
What is the clinical significance of transcription factors?
Transcription factors play crucial roles in various diseases and are potential therapeutic targets for cancer, developmental disorders, and neurodegenerative diseases.